Starting a MERN project is different from Ruby on Rails, Rails spoonfeeds you with their documentation and powerful generate commands while MERN kind of expects you to know what you are doing, but you still have access to NPM and NPX. Our MERN application needs to have a frontend and backend directories, so we start off by making the frontend, then the backend.
Frontend
We want to make a directory to hold both of our applications mkdir SWB_ERP, move to the directory and create the frontend with NPX: cd SWB_ERP and npx create-react-app swb-erp-frontend, move into that new directory and start npm: npm start
Axios is going to make our calls to the backend server, so go ahead and install axios: npm i axios. Inside /src, create another directory called components, and inside components create a file called axios.js. This is the same file where we would list the Heroku server, where our backend would reside, once we push the frontend to Firebase. Fill axios.js with the code below:
import axios from 'axios'
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: "http://127.0.0.1:3012"
// baseURL: "https://swb-erp.herokuapp.com"
})
export default instance
Back to App.js where we remove most of the demo code and we make a component that's going to make our call to the backend server once we have it running.
import './App.css'
import { useState } from 'react'
import axios from './components/axios'
function App() {
const [title, setTitle] = useState(null)
const Test = () => {
async function fetchData() {
const req = await axios.get("/test")
setTitle(req.data.title)
}
fetchData()
return <h1>{title}</h1>
}
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<Test />
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App
The backend is not able to take this get request, so the next stage is working on the backend.
Backend
Start up another terminal, cd into the projects's parent directory, make the directory: mkdir swb-erp-backend, change to that directory cd swb-erp-backend, and create a package.json file using npm: npm init. The only thing we need to change from the default is the entry point, to server.js, but feel free to add a description or author name.
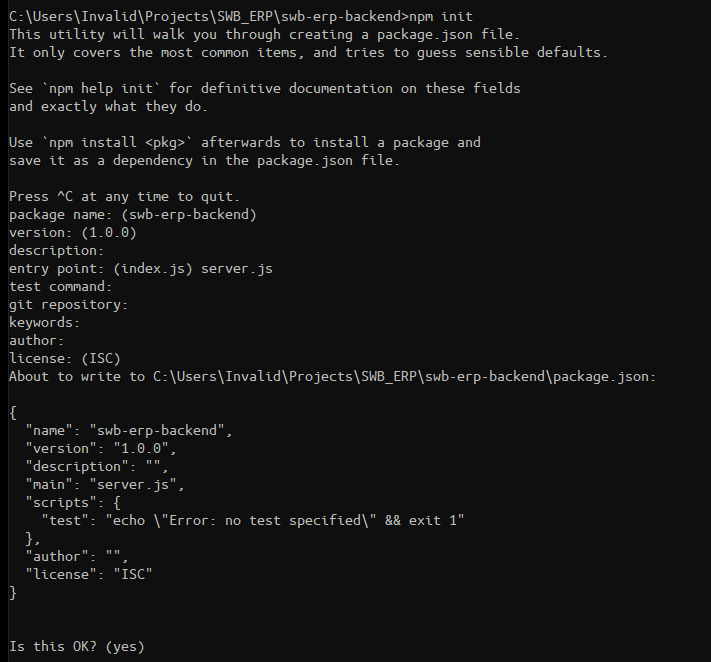
Chances are we will be pushing the backend to Heroku, so you can git init in the swb-erp-backend directory and add node_modules to the .gitignore file.
Open the newly created package.json file and add "type": "module" and "start": "node server.js" to the file.
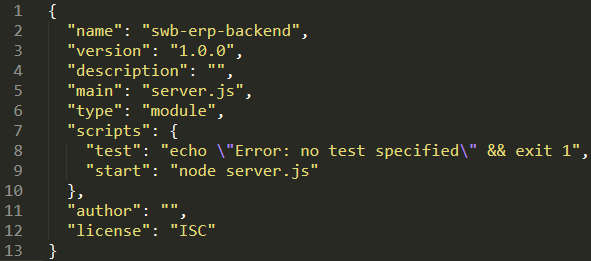
We will need mongoose, cors, and nodemon in addition to expresss. Install with npm i express mongoose nodemon cors.
Create a server.js file and add the following:
import express from 'express'
import mongoose from 'mongoose'
// config
const app = express()
const port = process.env.PORT || 3012
// endpoints
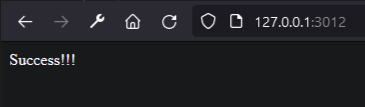
app.get("/", (req, res) => res.status(200).send("Success!!!"))
app.listen(port, () => console.log(`Listening on: 127.0.0.1:${port}`))
We use nodemon to run the application: nodemon server.js. Then navigate to 127.0.0.1:3012 in the browser to ensure everything is working.
Now we need our backend server to return some real data. Mongoose needs a Schema to map to MongoDB. Create a file dbEstimates.js and fill the file with the following:
import mongoose from 'mongoose'
const estimateSchema = mongoose.Schema({
job: String,
cost: Number,
date: Date,
approved: Boolean,
tasks: [{name: String}]
})
export default mongoose.model('estimates', estimateSchema)
The mongoose docs offers other ways to write the code, so it may be beneficial to look at them.
Listed below, we have a few extra endpoints. The /test is just to test the endpoint with some local data, whereas /estimates and /estimate are connecting to MongoDB and retrieving any data in the database. The Post method is going to populate our database, so it can be used on our application or used with the Postman application to push data to our backend API and send it to MongoDB.
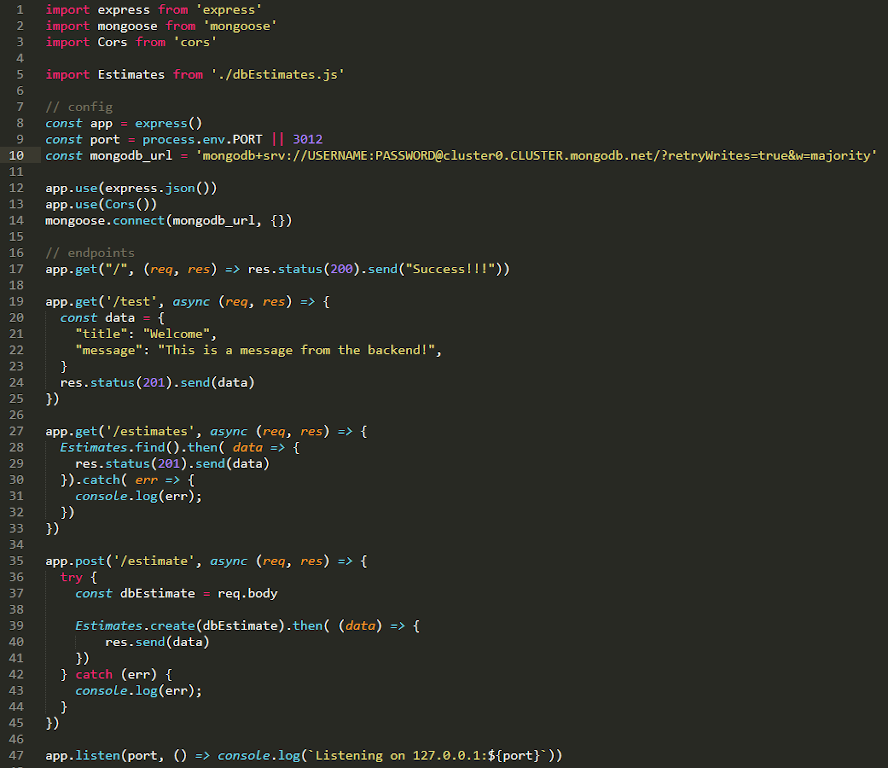
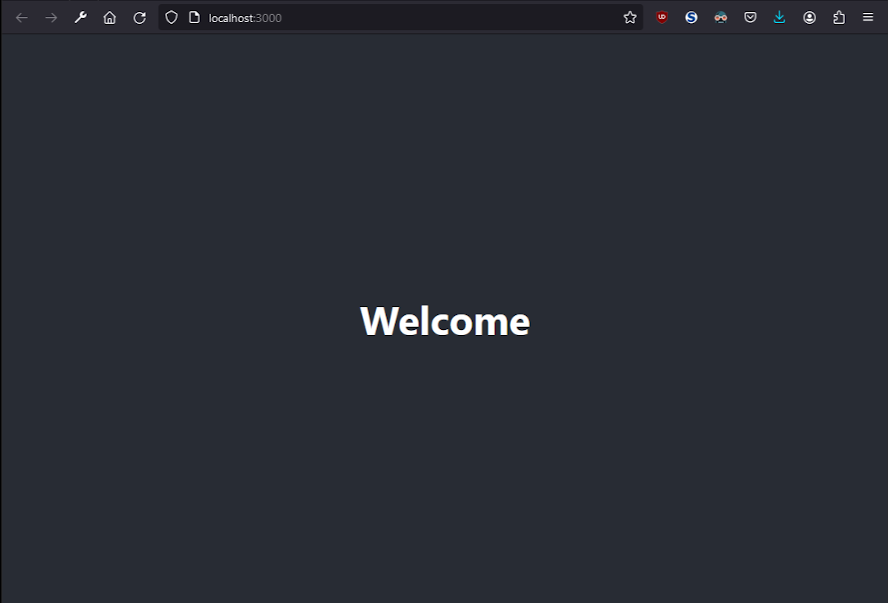
The frontend should be able to make our original get request to /test, so the browser should be displaying "Welcome". Just change the get parameter to /estimates and you will be making calls from MongoDB.